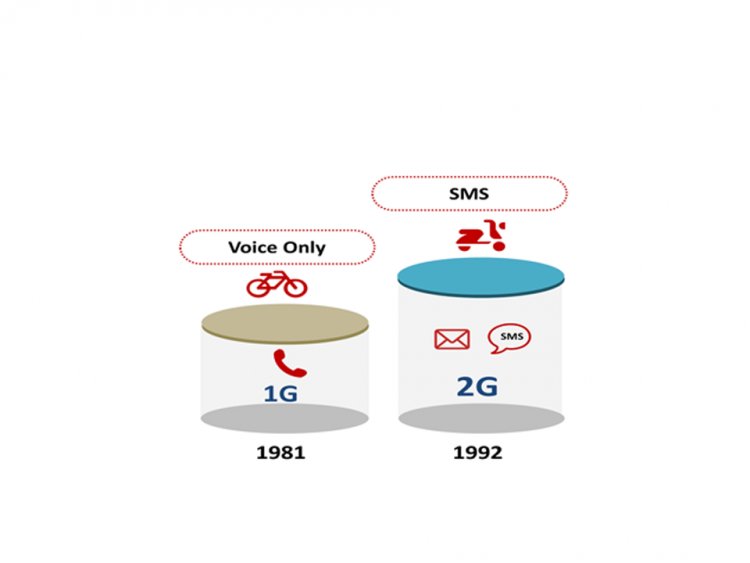
Second Generation of Mobile Network
The second generation of mobile networks is one step ahead of the first. 1G only offers analog transmission and voice communications, whereas 2G is entirely dependent on digital transmission. The capabilities we use, like SMS, MMS, conference calls, and call holds, are all made possible via 2G cellular technology.

Introduction:
The original 1G was designed purely for phone conversations, allowing individuals to keep in touch with one another. However, in terms of SMS, call quality, call holds, and conference calls are not features of 1G. 2G (second generation) is a step forward from 1G. With the addition of high bandwidth, 2G can send data at a rate of 64Kbps. Essentially, we may refer to The next generation of 1G as 2G.
What does phase 2G mean?
This was meant to convert the 1G analog circuit to a digital circuit. Many of the fundamental features that we still use today, such as internal roaming, SMS, conference calls, call hold, and service-based invoicing, were introduced by 2G.[1]
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM ) 2G technological mechanism has a frequency of 1.8 GHz and a bandwidth of 64Kbps across the core network Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and the normal circuit-switched telephone network.
What is the backstage story of 2G?
The working on the 2G began in 1980 and was expanded in 1999. The primary distinction between 1G and 2G is that 1G uses analog radio transmissions, whereas 2G uses digital radio signals. Multiple users can be served on a single channel by multiplexing is the capability of 2G.[1]
What Technology Used in 2G?
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is the foundation of 2G cellular technology, which is centered on standards of European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), Time Division Multiple Access(TDMA) IS-136, and Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA).[2]
How does 2G works?
It employs density (compression) and decompression techniques to protect digital information. The partitioning of this narrow band into three-time slits tends to increase the frequency band's total capacity.
What benefits does 2G offer?
- It is possible to transport data at rates of up to 64 kbps.
- Digital signals are used instead of analog signals.
- SMS and MMS are permitted services (Multimedia Message)
- On the condition that high-quality voice calls are made
- It has a frequency range of 30 to 200 kHz.
What are the drawbacks of 2G?
- If network coverage is not accessible in a given place, there will be a signal difficulty.
- It is incapable of handling complicated data such as video.
Conclusion:
The 2G technology is the following generation of 1G, which was created to address the shortcomings of 1G. The 1G merely allows users to make audio conversations with less security, but the 2G permits the services that we now use: conference calls, call holds, SMS, and service-based invoicing. The data is transferred at a quicker rate with 2G than 1G.
- 5G, G.V.G.V.G.V.G.V.; Available from: http://net-informations.com/q/diff/generations.html.
- Available from: https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/2g-second-generation.

 admin
admin