Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation is a technology that mimics the activities of a human while engaging with digital systems. RPA is highly scalable and readily adapts to ever-changing corporate contexts.

Introduction:
Today's business model has been changed automatically. Robotic automation in business operations is increasing in popularity. What option do you have when a high-value job can now be handled at a lower cost and more efficiently? You should choose a process that produces fewer errors at a lower cost. RPA is defined as software-related technologies such as service applications and IT applications that use software robots to automate manual operations based on duplicate and transactional processes.
What is RPA (Robotic Process Automation)?
RPA is a technological claim that is managed by business logic and organized inputs that is aimed at automating business activities. A business can programmer software, known as a "robot," to release and interpret applications for processing transactions, changing data, triggering replies, and interfacing with other digital systems. Making use of RPA tools.[1]
What is the history of RPA (Robotic Process Automation)?
ML is a technology that contributes to this success (machine learning). The ML will eventually open the way to RPA development. In 1959, Arthur Samuel founded the ML. RPA is a combination of various technologies; all of these technologies are integrated under one set of tools for various automation. Because its development began in the 1990s, the term "RPPA" first appeared in the early 2000s.
Who Invented the RPA (Robotics Process Automation)?
Phil Fersht, founder and chief analyst of HFS Research, coined the term "RPA." Technology has grown steadily until 2018 when it gained momentum as businesses embraced digital transformation and skills on the RPA platform increased. Alastair Bathgate and David Moss founded their own company to provide a novel approach now known as robotic process automation, or RPA.
What is the scope of Robotic Process Automation?
The RPA can handle tasks such as transition, data processing, copying and pasting, and any other activity that is heavily influenced by laws and schedules. The robot software operator can perform tasks such as retrieving client profiles, supporting, and ordering information from various corporate systems and applications.
What can RPA accomplish for your company?
Office workers spend up to 80% of their time filling out paperwork, using repetitive calculations, and processing orders. According to some estimates, a call center employee may need to contact six or more different editors to resolve a one-on-one meeting. Many of these processes are eligible RPA candidates.
RPA can be used to perform tasks without human interaction from start to finish. This is defined as "unlocked automation." RPA can also be useful for activities where personal contact is desired but at the same time at least some work can be done automatically. Such activities are called "household chores." In this case, robots serve as digital assistants to individuals.[2]
What is the process of RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the use of computer software "robots" to perform duplicate, law-abiding digital tasks such as filling in the same information in multiple locations, backing up data, or copying and pasting. Allows organizations to submit additional administrative functions to robots that can handle it efficiently and with complete compliance.
This enables the company to increase cost productivity by reducing efficiency and improving accuracy. Remarkably, it directs attention away from normal work and work that requires judgment, motivation, and interpersonal skills. You can read our previous blog post for more information on what RPA is; in this case, we will look at how the RPA works.
What are the advantages of the RPA in business?
Gains inefficiency:
RPA can accomplish jobs more quickly and efficiently than people, and at a lesser cost.
Error elimination:
Computers just do what they are taught. They don't make a lot of mistakes, as people may.
Enhanced agility:
According to Ken Weilerstein, analyst and consultant at The Analyst Syndicate, RPA frequently helps an organization to more quickly absorb business process changes.
Increased use of people's power:
RPA frequently enables organizations to move workers' attention from low-value activities to higher-value ones that provide a better customer experience and, as a result, boost revenue growth.
Enhanced employee engagement
Because RPA bots do repetitive and oftentimes monotonous, activities inside the organization, employees may devote more of their time to higher valued work, resulting in more engaged employees.
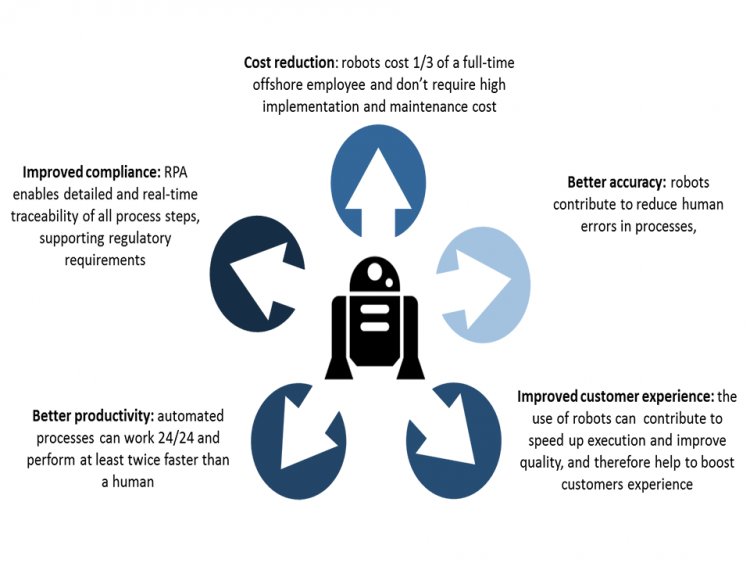
Customer satisfaction has increased:
Customers can find automated processes in organizations as automation can create a faster and better feeling. A bot, for example, may access and retrieve information in real-time in response to a client request, eliminating the need to ask the customer to wait.
Process standardization
Even when organizations enhance their procedures, it is difficult to verify that human workers follow the predetermined steps every time in every single office location.
Business Continuity Assistance:
According to Martelon, organizations may utilize RPA to assist support their business continuity (BC) strategies by developing bots that can take on duties traditionally done by outsourced services in the event such services go down.[3]
What are the disadvantages of RPA in business?
Broadening technology:
As organizations add more bots to do more activities, they risk building an unmanageable collection that is difficult and expensive to manage and maintain.
Added complication:
Similarly, RPA may result in layers upon layers of software if it is not properly documented, controlled, and governed, according to Weilerstein. It adds complexity, which may make company improvements more difficult to implement.
Problematic processes are magnified:
Experts warn that organizations that do not analyses and, if required, re-engineer and optimize processes before automating them run the danger of automating problematic operations. This entails increasing any inefficiency, faults, or other flaws in the process in the first place. It also adds expenditures, which may cancel out any anticipated ROI and bring additional dangers.
Transformation thwarted
According to Martelon, executives that view RPA as a tactical point-by-point solution rather than a tool that is part of a broader strategy will reap fewer rewards. Enterprise executives who want RPA to help them achieve their digitization goals must have a strategic strategy for prioritizing their automation initiatives and understand how those projects fit into their larger strategic aspirations.[3]
Conclusion:
RPA has transformed human existence in distinct industries. Businesses use the RPA Robotic Process Automation technology to automate knowledge-based, professional service operations that do not require human involvement. At the same time, it serves as a key advocate for the mainstream interpretation of labor arbitrage.
- Boulton, C. What is RPA? A revolution in business process automation. September 3, 2018.; Available from: https://www.cio.com/article/3236451/what-is-rpa-robotic-process-automation-explained.html.
- ; Available from: https://www.nice.com/rpa/rpa-guide/what-is-rpa/.
- Pratt, M.K. What are the advantages and disadvantages of RPA? ; Available from: https://searchcio.techtarget.com/feature/What-are-the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-RPA.

 admin
admin