Artificial Weak Intelligence
There are three types of AI based on the capabilities. Narrow artificial intelligence or Weak artificial intelligence is restricted to its assigned tasks.

Introduction:
Weak AI is the type of AI that is designed to finish a specific task and the training algorithm is premeditated to finish a definite assignment, with some information attained from that effort not being automatically or robotically functional to other tasks. The vast majority of today's AI applications in usage may be classified as weak AI. Weak AI, often known as narrow AI, is a type based on the capabilities of artificial intelligence that is restricted in scope.
what is Weak AI or narrow AI?
Weak AI is the type of artificial intelligence that is restricted to a specific area. Weak AI, also known as narrow AI, is a kind of artificial intelligence that is meant to do specialized tasks such as facial recognition, automobile driving, speech recognition/voice assistants, and web surfing. It is extremely fast and precise in completing the task for which it was created.[1]
It is designed to mimic human intellect. It has the prospective to advantage society by automating time-taking operations and analyzing data in ways that individuals cannot always do. Weak AI can be compared to strong AI, which is a hypothetical type of computer intelligence that is equivalent to social intelligence.
Weak AI just obeys and is constrained by the rules that have been imposed on it, and it is unable to depart from them. An excellent example of faulty AI is individuals in a video game who operate realistically inside the framework of their game character but are unable to do anything beyond. Narrow AI is another name for weak AI.
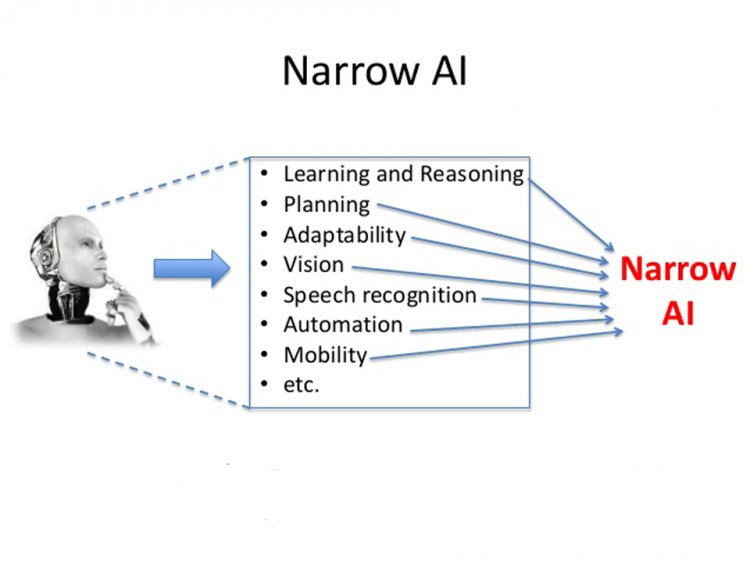
What are some common examples of narrow AI?
- Voice supporters that are digital (Siri, Alexa):
Digital voice supporters like Siri and Alexa, which are occasionally mentioned as the finest instances of weak AI, are models of weak AI that we trust every day. To function properly, the AI identifies data and replies to requests at a breakneck swiftness.
- Engines that make recommendations:
Narrow AI is exemplified by these recommendation engines. These reference engines are instances of narrow AI, whether Netflix informs you what film to view next or Amazon or even other retail websites give you helpful information on what else you could be interested in purchasing.
- Search engine:
Google and other search engines are other examples of AI that aren't very good. When you write your question into the rectangle, the algorithm goes to work categorizing it and returning replies from its large database.
- Chabot’s:
You've undoubtedly talked to AI if you've ever talked to a firm, whether it's your bank, internet service provider, or favorite’s e-commerce site. Most of the time, chat features are an AI algorithm that handles simple questions, allowing people to focus on greater tasks.
- Vehicles that drive themselves:
Weak AI is AI that allows cars to run without a humanoid driver. Algorithms are used to fulfill pre-programmed operations. Because an AI lacks the complete intellectual powers of a human brain, the difficulty is to program and teach it to distinguish any conceivable road hazard or condition that the car may meet.
- Recognition of images and voice:
Image recognition, which aids radiologists with detecting illness inpatient scans, is a unique important method narrow AI is making an effect in healthcare. Image recognition is also hampered by poor AI in other businesses. Speech recognition and translation systems like Google Translate are also affected.
- Analytics and predictive maintenance:
Predictive analytics employs a specific type of artificial intelligence. It uses data, algorithms, and machine learning to analyze prior data and predict a likely future event. In warehouses and other locations where heavy equipment is utilized, AI can help detect upkeep concerns that need to be handled before a mechanism breaks.
- Robots:
At the moment, robots do not have their own minds. Drones and sweatshop robots have limited AI and can solitary carry out a restricted range of tasks that have been programmed for them. During the restricted, delivery bots were extremely beneficial in observing with social distancing requirements and as disinfecting robots.[2]
What are the advantages of narrow or Weak AI?
- Narrow AI systems may excel at a specific task, frequently outperforming humans. For example, a weak AI system built to detect cancer from X-ray or ultrasound pictures may find a malignant lump in images faster and more correctly than a skilled radiologist.
- Meanwhile, a predictive maintenance platform might evaluate incoming sensor data in real-time, something that would be nearly hard for a single person or group of people to perform, and forecast when a machine component would break.
What are the disadvantages of narrow or weak AI?
- Narrow AI systems can only perform what they're programmed to do and make judgments based on their training data. For example, a retailer's customer-service Chabot may answer queries about shop hours, item pricing, and return policies. However, unless the bot's designers took the effort to teach the bot to reply to such queries explicitly, a query regarding why a given product is superior to a comparable one would certainly baffle the bot.
- Meanwhile, AI systems are prone to bias and frequently provide inaccurate findings that are difficult to explain. Complex models are frequently trained on enormous volumes of data, far more than their human developers can handle. Biases or errors in large volumes of data are common.
- One of the problems of weak AI, apart from its limited skills, is the risk of injury if the system flops. Consider a self-driving car that miscalculates the location of an approaching vehicle, causing a tragic collision. A terrorist employing a self-driving car to detonate bombs or bullets in a public area is an example of how the technology might be used to cause harm if it is misused.
- One issue linked to inadequate AI is indeed the lack of jobs caused by the automation of an increasing number of tasks. Will unemployment rise, or will civilization find new ways for people to earn money? Even though the prospect of a large number of individuals losing their jobs is worrisome, proponents of AI say that as AI is becoming more extensively employed, new professions will emerge that we cannot now imagine.
- The shortage of jobs induced by the digitization of an expanding number of tasks is one concern associated with insufficient AI. Will there be a growth in unemployment, or will society develop new methods for individuals to make money? Despite the fact that the idea of a significant number of people losing their employment is concerning, proponents of AI argue that as AI becomes more widely used, new vocations will develop that we cannot now foresee.
Conclusion:
Machine learning artificial intelligence is a vast discipline of comp science concerned with a machine's capacity to generate logical behavior related to external inputs. AI aims to develop computers that can do activities that would otherwise need human intellect.
- Narrow Artificial Intelligence (Narrow AI). July 19, 2021; Available from: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/32874/narrow-artificial-intelligence-narrow-ai.
- What is Weak (Narrow) AI? Here Are 8 Practical Examples. May 27,2021; Available from: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-weak-narrow-ai-here-8-practical-examples-bernard-marr.

 admin
admin