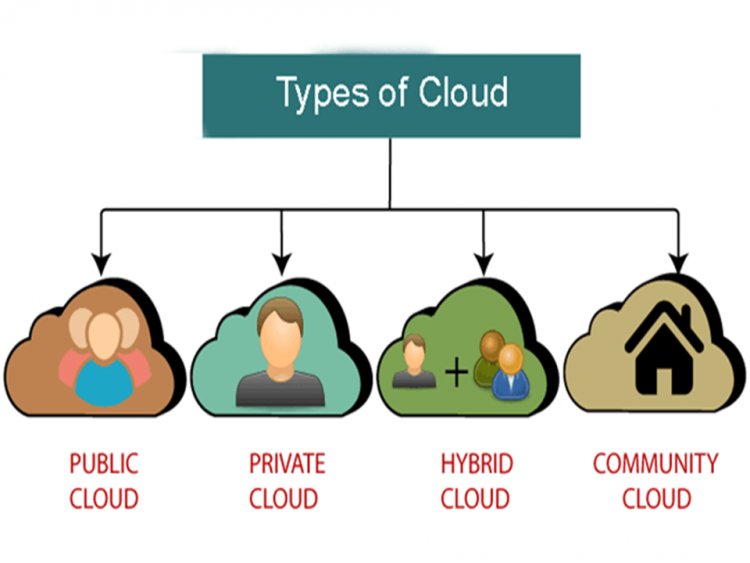
Types Of Cloud Computing
There are 4 main types of cloud computing: private cloud computing, public cloud computing, hybrid cloud computing, and community cloud computing.

Introduction:
Cloud computing refers to the process of storing and retrieving data over the internet rather than on a hard drive. Cloud technology is the Internet-based distribution of services linked to servers, databases, storage, software, networking, analytics, and intelligence. There is no limit to the amount of data that can be stored in the cloud thanks to virtualization, which is quick and efficient and provides low-cost software. There are different types of cloud computing. Each type has its own properties that the user can use according to its requirements.
How many types of a cloud deployment?
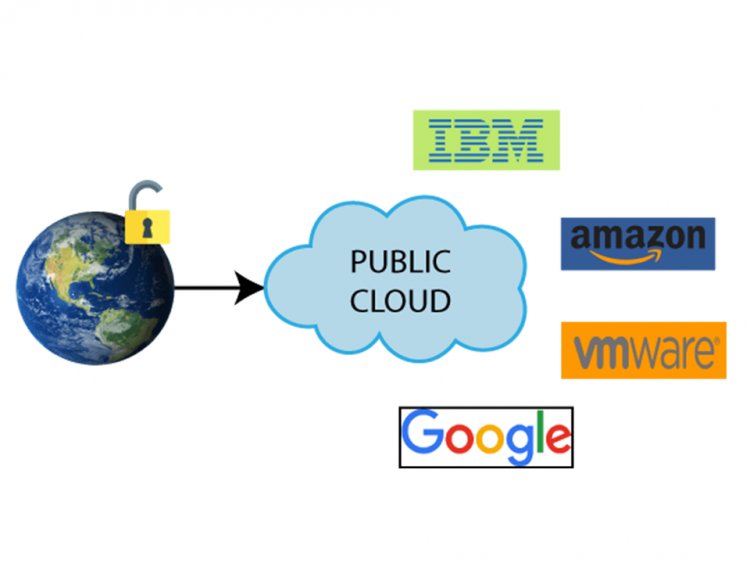
- Public cloud
In this type of model, all the services that are on-demand and the infrastructure are managed by a third party. The third-party manages all its computing services and shares them with multiple organizations with the help of the internet. On a monthly or pay-per-use basis, public cloud services provide many services such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS).
The public cloud makes offers for commuters that anyone can purchase. Typically, the use of the public cloud is possible for many users.
Pros of Public Cloud computing:
- Management of the infrastructure:
It features a straightforward infrastructure. Public clouds are a forthright and agreeable solution for practice since they are managed by a third party.
Because the software is accomplished by a third party, there is no requirement for a company to construct its own.
- Minimal Investment:
Because you only compensation for the services you use, there is no need to capitalize in software or hardware.
- Uptime:
Expect to be up and running around the clock, seven days a week. The public cloud networks are large, meaning that they are reachable and that they can trust on faster reaction times.
Cons of Public Cloud computing:
- Less safety:
Data privacy and security are dangerous. Public clouds don't tell clienteles where their data is reserved or who has admission to it when data access is straightforward.
- There are fewer options:
There aren't a proportion of options. Public cloud corporations frequently service standard choices as a one-size-fits-all technique. It's conceivable that a corporation won't be intelligent to meet a one-of-a-kind demand.
- less control:
When you subcontract to the public cloud, it's factually out of reach. Any IT management confirmation and other workings are outsourced to an assemblage not involved in day-to-day operations.
- Private cloud
Private clouding contains all the features provided by public cloud computing with the addition of scalability and also self-service having proprietary architecture. We can also say that all its services must be useable at a time for only one customer or organization. It is also called the internal corporate cloud because it fulfills all the requirements of an organization ware public cloud delivers services to all the organization.it provides you high level of privacy and security.it combines resources all the physical hardware in a shared pool by using virtual reality.
Pros of Private Cloud Computing:
- Controls:
Higher-quality data, users, and material benefit controls. When it originates to the on-premise arrangement, the initial hardware spending is significant.
- Security:
The cloud is owned by a single customer. As a result, the infrastructure and systems may be organized to provide the highest level of security
- Exceptional Results:
Private clouds are commonly deployed organizations' intranet firewalls, guaranteeing great network presentation and efficiency.
- Customization is simple:
The company might simply makeups and downs to its hardware and other resources.
- Compliance:
Compliance is straightforward to achieve in private clouds.
Cons of Private Cloud Computing:
- Cost:
The operational costs would comprise personnel customers as well as hardware developments on a regular basis. Companies subcontract private cloud operating expenditures that will include per-resource use and are subject to modification at the service provider's pleasure.
- Underutilization:
The subscribed resources may be underutilized in some cases. As a result, maximizing the use of all resources is difficult.
- Capacity ceiling:
There could be a capacity ceiling to handle just a specific number of computers or memory due to the physical equipment restrictions with the service provider.
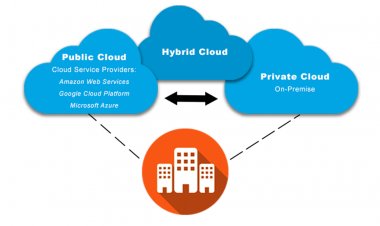
- Hybrid cloud
We can say that hybrid cloud computing mixture or a combination of public and private cloud computing’s. It has a flexible configuration according to the requirements and also includes private assets and many other applications with the aim of balancing the possible variables, from resources usage to compatibility with legacy applications. The organization is able to take a passed approach to public cloud adoption for their transition needs based on legacy hardware, proprietary data, and other potential reasons.in some cases, hybrid computing also offers the solution between the benefits of practical limitation of cloud capabilities and modern cloud technology when high-performance computing is involved.
Pros of Hybrid Cloud Computing:
- cost-cutting:
A hybrid cloud is accessible it can provide somewhere to stay future changes in business objects at an inferior cost.
- Control, performance, and scalability are all in a unique balance:
Only hybrid cloud knowledge can union the advantages of both public and private servers.
- Timeliness of deployment:
This coordination isn't finally open to the open, company IT supervises will be able to decrease the potential, making statistics transfers earlier and easier.
- Business resiliency:
Cloud computing not only links new and old systems, but it also allows organizations to develop an overall structure that matches the specific needs of a company.
Cons of Hybrid Computing:
- Security overly complicated
Because hybrid clouds are so complicated, safeguarding effective, long-term security is difficult. You should be organized to deal with this procedure anytime you put dangerous data into your mixture cloud.
- Issues with visibility:
Maintaining visibility across a vast hybrid cloud was problematic for many IT personnel.
- Community cloud
Community cloud computing denotes the shared cloud computing services by targeting the limited set of employees and organizations. The principle on which the community could be organized can vary but the member of the community cloud mostly shared. Same criteria for security, privacy, performance, and compliance Members of the community may decide to use a process that they (rather than the provider) use to vet people seeking access into the community.
Pros of Community cloud computing:
- Scalable and adaptable:
Our cloud environment is versatile and scalable since it is accessible to all users. It enables users to tailor papers to their own requirements and wants.
- Security:
The cloud service is more secure than the community cloud, while the cloud infrastructure is less secure.
- Infrastructure pooling:
The community cloud enables several businesses to share cloud resources, infrastructure, and other features.
Cons of Community Cloud Computing:
- Not the best option:
For every company, community cloud is not the best option.
- Data agreement is taking longer than estimated.
- All public members portion the same set quantity of data storing and connectivity.
- The cost of using a community cloud is upper than that of using the public cloud.
- Challenging
It's challenging for companies to share responsibility.
Conclusion:
Cloud computing offers low-cost software to you. It offers state-of-the-art internet security. Always available, and automatically scales to meet rising demand with allows for pay-per-use also. Control and interfaces can now be accessed over the internet API.one can choose cloud computing by keeping in mind the following points:
- Each model's running costs
- Your network's traffic demand
- When the system should be updated
- The internet connection quality in the neighboring area

 admin
admin