Network Topology
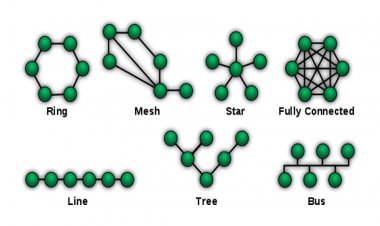
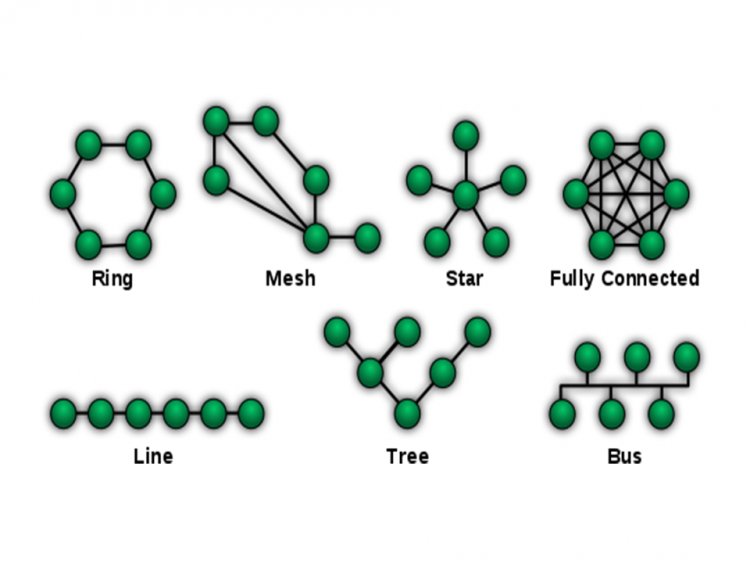
The Network Topology refers to stations connected to a network connection. There are several types of network topologies, including ring topology, bus topology, mesh topology, hybrid topology, star topology, and tree topology.
Introduction:
The word "topology" denotes the joining between endpoints or stations linked to a network connection, as well as the arrangement of the system on a computer. In the different types of offices, the data needs to be shared, so the devices in the office are connected to each other through networking. The manner in which these devices are connected is called network topology. There are several types of network topologies, including ring, bus, mesh, star, and tree topologies.
What exactly is network topology?
Network topology is the arrangement or manner in which the devices are connected to each other and how the data is transformed between the nodes. It can also be defined as the systematic description of a network.
What is the significance of network topology?
The goal of topology is to help people understand the important things in life. also allows us to understand the different elements in the network, in which way the devices are connected, where they connect, and how they share data with one another.
What is the background of network topology?
Johann Benedict Listing coined the term topology in the nineteenth century, but the concept of a topological space did not emerge until the first decades of the twentieth century.
How many different types of topology are there?
There are different types of topology.
- Bus Topology
- Ring Topology
- Star Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Tree Topology
- Hybrid Topology
Bus Topology
In this topology, every computer in the connection is associated with a solitary cable. The bus topology has two endpoints.[1]
The Advantages of Bus Topology:
- When associated with further network topologies, the extent of cable mandatory is the lowest.
- Use it for minor networks.
- It is simple to grasp.
- Linking two wires together is a simple way to grow.
Advantages and disadvantages of bus topology:
- If a cable breaks, the complete network fails.
- When network transportation is high or there are a lot of devices, network performance is affected.
- The chain has a restricted length.
Ring Topology
In this topology, each computer is linked to another computer, with the last computer connected to the first, establishing a ring.[1]
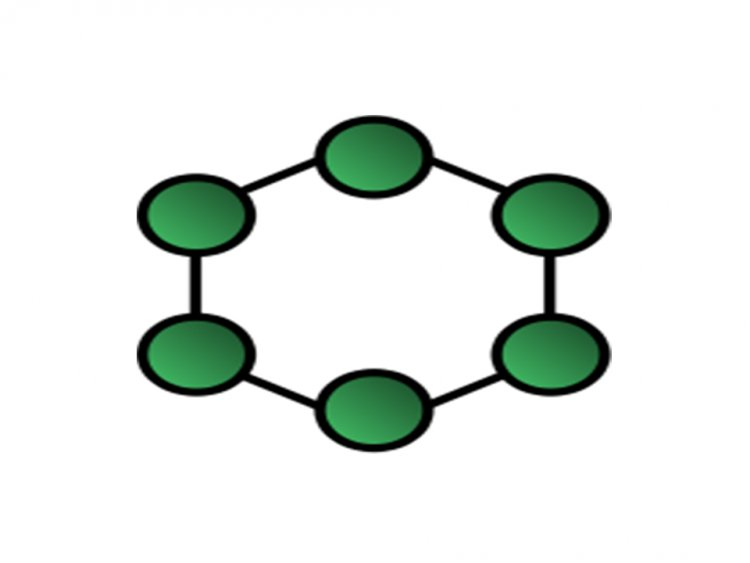
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- Because individual nodes with tokens may send data, increasing traffic or adding extra nodes have no consequence on the transmitting network.
- Connecting and increasing it is inexpensive.
Disadvantages of ring topology:
- In-ring topology, troubleshooting is puzzling.
- Adding or removing computers disrupts network activity.
- The failure or problem of one computer disrupts the entire network.
Star Topology
In this topology, all computers are linked to a single hub. This hub is known as the basic or central node, and all new nodes are linked to it.[1]
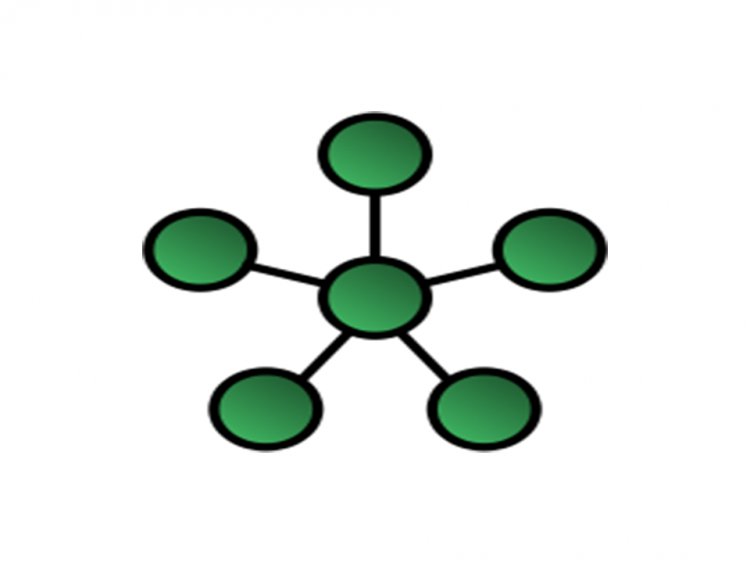
Advantages of Star Topology:
- Reckless enactment with a minor number of nodes and negligible network traffic.
- The hub is easily upgradeable.
- It is simple to troubleshoot.
- It is simple to set up and modify.
- Only the failing node is impacted; the remaining nodes can continue to function normally.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
- The installation fee is exorbitant.
- It is costly to use.
- Because all nodes depend on the hub, if it fails, the entire network comes to a halt.
- The hub determines performance, which is dependent on its capacity.
Mesh Topology
Every device in this architecture is connected point-to-point. All of the gadgets are linked to one another. Mesh networks link n devices using n (n-1)/2 physical channels.[1]
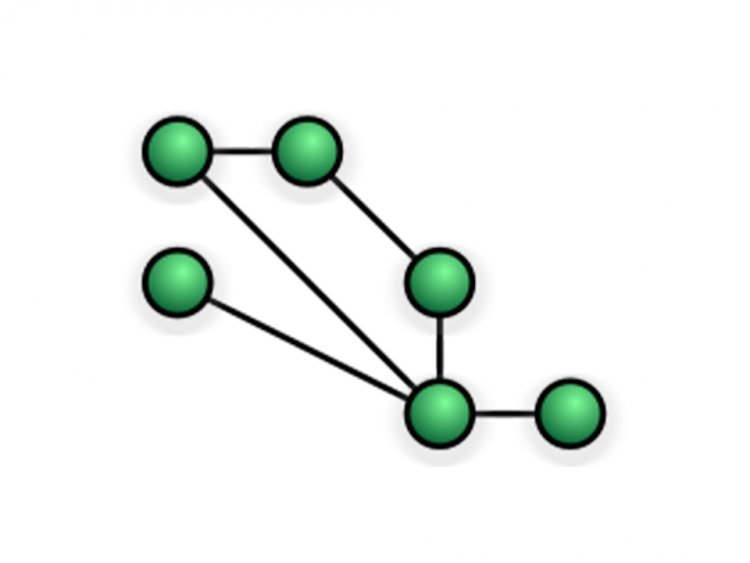
There are two ways to send data via the mesh topology:
- Routing
- Flooding
The Topology of Mesh: Routing
Routing logic is engaged by nodes in agreement with network needs. As an example, routing logic may be used to direct data to its target via the shortest possible path. Otherwise, routing reasoning that is aware of faulty links and escapes certain nodes, etc. We may even include routing reasoning to re-configure broken nodes.
Flooded Mesh Topology
Because overflowing sends the identical records to all set-up nodes, no routing reason is necessary. The network is strong, and data loss is improbable.
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
- Each link is capable of carrying its own data load.
- It's tough.
- The fault is quickly identified.
- Secures and protects your privacy.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
- It is tough to install and configure.
- Cabling is more expensive.
- Bulk cabling is required.
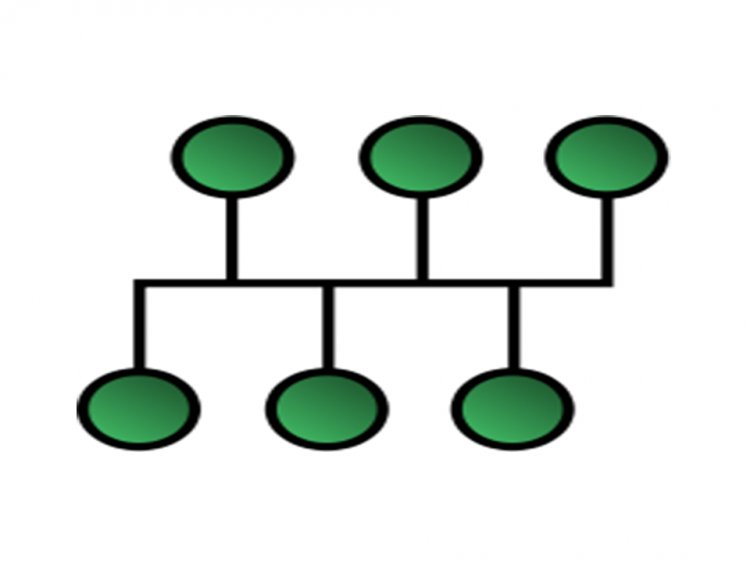
Tree Topology
In this topology, all of the devices are connected in such a way that they create a hierarchy. It's also referred to as hierarchical topology. There should be at least three stages in the hierarchy.[1]
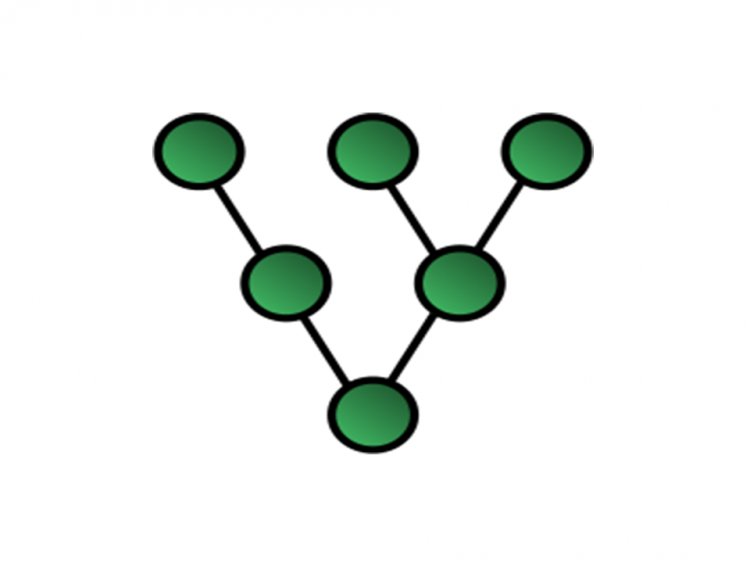
Advantages of tree topology:
- Both the bus and the star topologies are stretched.
- Node enlargement is both doable and modest.
- Simple to manage and uphold.
- Error recognition is simple.
Disadvantages of tree topology:
- Extremely cabled
- Repairs become tough when extra nodes are announced.
- When the central hub fails, the whole network fails.
Hybrid Topology
It is a hybrid of two or more topologies. For example, if star topology is used in one department of an office and ring topology is used in another, connecting both topologies results in a hybrid topology (ring topology and star topology).[1]
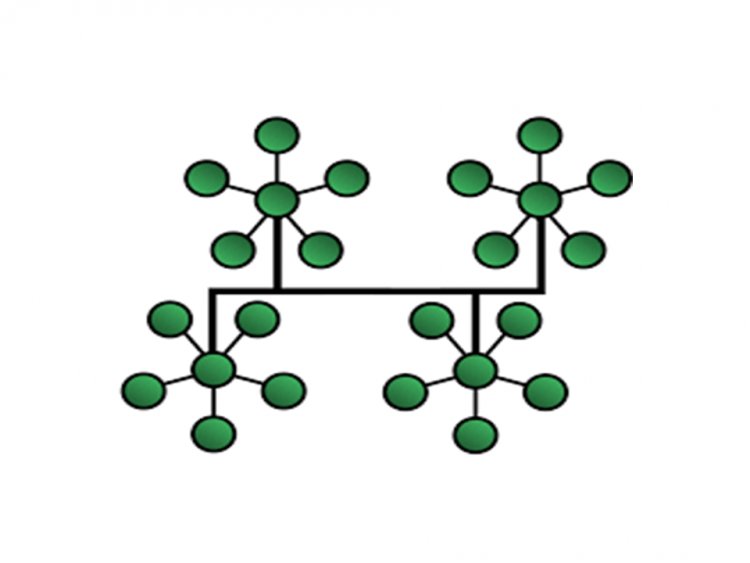
Advantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Trustworthy as It is simple to spot faults and troubleshoot them.
- Accessible in the sense that its size can be readily expanded.
Disadvantages Hybrid Topology:
- The design is intricate.
Conclusion
There are different types of network topology. One can use topology according to the type of connection and the working of the office. Each topology has its advantages and disadvantages. If the server gets down in the topology, it faces failure.
- Types of Network Topology. Available from: https://www.studytonight.com/computer-networks/network-topology-types.

 admin
admin