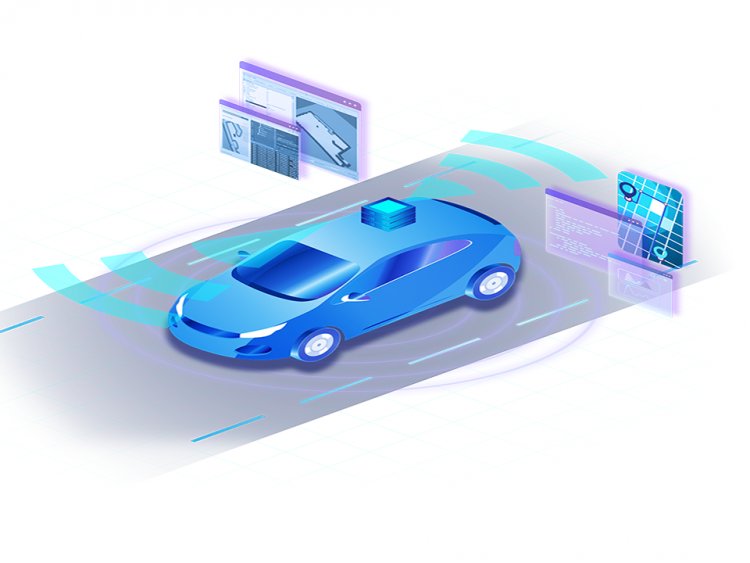
Autonomous car
An autonomous car is one that can sense its surroundings and operate without human intervention. A human passenger is not necessary for an automated car.
Introduction:
Do you read a book or watch videos while the car is in the chaos of traffic jams? All of this is made feasible by self-driving cars. Trucks, motorcycles, buses, and other autonomous vehicles do not require human control. They include all of the features that a car needs, such as driving and parking assistance, speed modification based on route circumstances, warnings on other cars, driving adaptations, and braking management.
What are autonomous vehicles?
Automation is now employed in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, utilities, cars, transportation, defense, and other institutions. Autonomous cars do not have anyone to monitor or drivers and use sensors, radar, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) to travel between places without the operator.[1] Autonomous cars can recognize their surroundings and function without the need for human intervention.

What is the history of the autonomous car?
Norman Bel Geddes developed the first self-driving automobile in GM's 1939 show. It was a remote-controlled electromagnetic field-guided electronic vehicle. Magnetized metal spikes installed in the road create electromagnetic fields. General Engines has complete this dream a reality by 1958. The car's front end was ready with "pick-up coils," which could notice current grace via a wire entrenched in the road. The current may be controlled to instruct the car to turn the steering wheel to the left or right.
In 1977, the Japanese expanded on this concept by deploying a camera system that fed data to a computer to process photographs of the road. This car, on the other hand, could only move at speeds of less than 20 miles per hour.
How do autonomous cars work?
AI is used to power self-driving automobiles (artificial intelligence). Self-driving vehicle developers employ enormous amounts of data from image recognition systems, as well as machine learning and neural networks, to design systems that can drive independently.
The neural networks recognize design and patterns in the data, and this data is approved into the machine learning algorithms. Images from cameras on self-driving cars are included in that data, from which the neural network learns to recognize traffic signals, trees, curbs, pedestrians, street signs, and other elements of any particular driving environment.[2]
What characteristics does a self-driving automobile have?
- Hands-free driving:
The center of the vehicle without the driver's hands on the steering wheel.
- Adaptive cruise control (ACC) has come to a halt:
It automatically maintains a selectable distance between the driver's car and the car in front.
- Steering with lane centering:
When the driver violates lane markers, it intervenes by automatically shoving the car into the opposing lane marking.
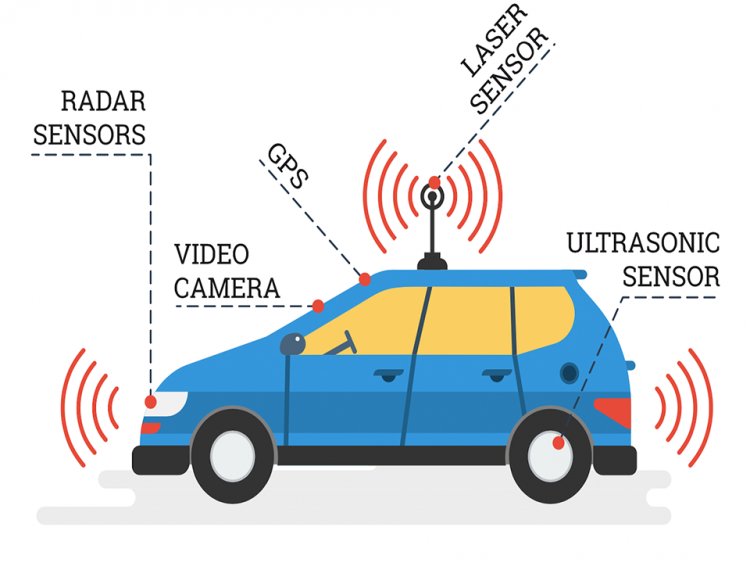
What are the different tiers of self-driving cars?
There are many levels of automation, and as the levels rise, so does the amount of the driverless car's individuality in terms of procedural control.
At level 0, the automobile has no control over its functioning, and the human driver is in charge of everything.
At level 1, the vehicle's ADAS (advanced driver assistance system) can aid or maintain the driver with steering, accelerating and braking, or both.
At level 2, the ADAS (advanced driver assistance system) can oversee steering, accelerating, and braking to some extent, but the human driver must maintain total attention to the driving environment throughout the voyage, in addition to performing the other essential responsibilities.
In some scenarios, the ADS (advanced driving system) can perform all aspects of the driving duty at level 3. The human driver, on the other hand, must be able to restore control when the ADS requests it. The human driver performs the essential activities in the remaining situations.
At level 4, the vehicle's ADS is clever enough to complete all driving errands autonomously in situations when human attention is not required.
Finally, level 5 entails full automation, in which the vehicle's ADS can do all functions in all conditions and no driving assistance from the human driver is necessary. The use of 5G technologies, which will allow cars to communicate not only with one another, but also with traffic signals, signs, and even the roads themselves, will enable full automation.[3]
What are the benefits of self-driving cars?
- To give improved road safety, fewer mistakes in compared to people.
- The annual death toll has been reduced.
- The number of traffic accidents has reduced.
- People who are unable to drive owing to issues such as age or disability may be able to use autonomous automobiles as more convenient modes of transportation.
What are the drawbacks of self-driving cars?
- Expensive
- Concerns about safety and security
- propensity for hacking
- Opportunities for others to work
- Sensors that don't work
Conclusion:
Autonomous vehicles completely alter human existence. It is now feasible to read a book while watching a video in the automobile. There are currently no legally operating, fully autonomous cars in the world. However, partially autonomous vehicles, such as automobiles and trucks with varying degrees of automation, ranging from brake assistance to lane change and parking assistance, with some models even having some degree of automated steering,
- Automation. 8 June 2021; Available from: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/32099/automation.
- Lutkevich, B. self-driving car (autonomous car or driverless car). Available from: https://searchenterpriseai.techtarget.com/definition/driverless-car.
- What is an autonomous vehicle? Definition and meaning. Available from: https://marketbusinessnews.com/financial-glossary/autonomous-vehicle/.

 admin
admin