Third Generation of Mobile Network
The third generation of mobile networks has surpassed the second. 2G is totally reliant on digital transmission, yet internet speeds are poor. The primary goal of 3G wireless technology is to allow for quicker Internet surfing and data downloads. All of the features we utilize, such as video calls and video conference calls and GPS are made possible by 3G cellular technology. 3G is also a highly secure network that allows for certification procedures.

Introduction:
People's voice calls and data transit capacity must be enhanced throughout time in order for them to use a diverse selection of apps. 3G is a development of 2G that combines all of the properties of 1G and 2G as well as some new ones. With 3G, an internet connection may be obtained from any location by getting a signal from the nearest tower without the usage of wires, at a reasonable cost. 3G, on the other hand, transmits data in the form of packets.
What does phase 3G mean?
This was meant to replace 2G In terms of coverage for voice conversations and text messaging with quicker internet access, owing to the capacity to transmit more data. 3G operates at frequencies ranging from 1.6 to 2 GHz, with a bandwidth of 2 Mbps. It is a packet network that transfers data in the form of packets.[1]
What is the backstage story of 3G?
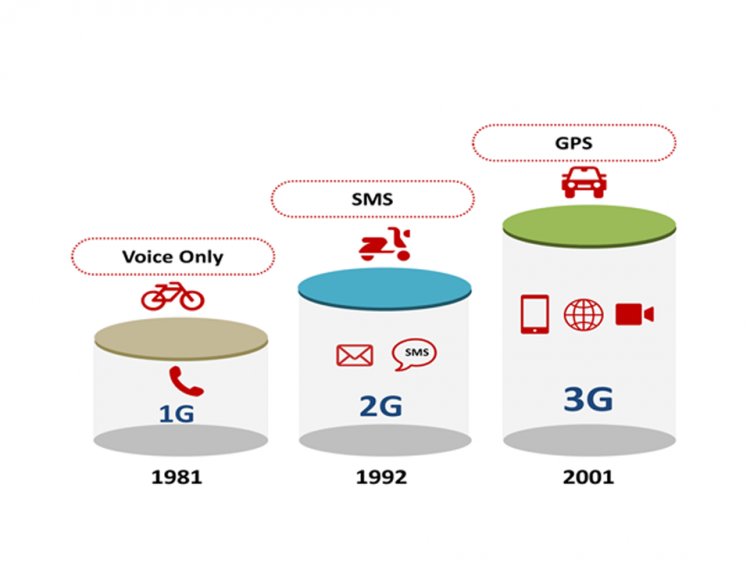
The development of 3G technology began in 1980 and was finished in 1999. The goals for third-generation mobile communication were to expand voice and data transfer capacity, enable a larger range of applications, and boost data transmission at a reduced cost.
What technology used in 3G?
The 3G fundamental network architecture is Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS). It combines 2G capabilities with new technology and protocols that allow it to transfer data at a quicker rate. It also features the standard Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) protocol, which works in conjunction with the Direct-Sequence Code Division Multiple Access (DS-CDMA) channel access technology and the FDD Frequency-Division Duplexing (FDD) scheme to deliver fast-moving and maximum capacity service. WCDMA is the utmost typically cast-off version of Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS). Japan's NTT DoCoMo industrialized it and utilized it as the cornerstone for its Freedom of Multimedia Access program.[2] The download speed in 3G is some time feels slower due to its dependency on the strength of the signal.
How does 3G works?
The third-generation facilities operate on “cellular" machinery; signals are transferred from one mobile tower to another mobile tower, and then the tower next-door or nearest mobile permits the signal to it. That’s why the digit of phone posts in the UK has enlarged rapidly. These posts safeguard that robust and trustworthy signal is accessible. It too implies that service may suffer as you travel about, as the signal means from tower to tower, and when a person travels also far-off away from the tower.[3]
What benefits does 3G offer?
- Increased data transfer rate
- There are multimedia services accessible.
- The internet is accessible from any location.
- International phone charges are reasonable.
- More emphasis is placed on security and dependability.
- Devices that are always linked
- Consumers will receive a high-speed network for data connection in order to offer interoperability across service
- Consumers can practice all of the accommodations at a similar time.
- Consumers can view the video.
- Appropriate for data-accelerated applications
- Customers will have access to the wireless broadband.
- A video sound and a huge MMS
- Continuous video streaming on smartphones
- It is considerably speedier than prior networks.
- A more data-intensive application can be created and used[4]
What are the drawbacks of 3G?
- It necessitates a variety of handsets.
- Inadequate bandwidth
- The power usage is rather significant.
- They need a closer base station and are therefore more costly.
- Spectrum license fees
- The exorbitant price of 3G phones
- The handset is capable of 3G connection rate and then prior network.
- A Third generation mobile phone is more expensive than a 2G cell phone.
- Data/roaming and voice, as well as collaboration, have yet to be deployed.[4]
Conclusion:
Smartphones with 3G capabilities offer the practical services, innovative features, and fast speeds that customers expect from a high-end phone. Because internet services are available, users may send more data at a quicker pace, increase voice and data transfer capacity, enable a wider range of applications, and raise data transmission at a lower cost. 3G has transformed the world into a global village, with everyone linked to their loved ones by phone in any part of the world.
- 5G, G.V.G.V.G.V.G.V.; Available from: http://net-informations.com/q/diff/generations.html.
- Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA). 21 October 2012; Available from: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24282/wideband-code-division-multiple-access-wcdma.
- Available from: https://3g.co.uk/guides/3g-what-is-3g-explained-in-simple-terms.
- 3G advantages and disadvantages. Available from: https://www.ecstuff4u.com/2018/05/3g-advantages-and-disadvantages.html.

 admin
admin